Professor Wang Zhouping's team from the School of Food Science and Technology of Jiangnan University published a review paper titled "of in the of" (Research Progress of Aptamer Sensor Technology in the Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria) in Food.
Summary:
In recent years, foodborne pathogenic bacteria have attracted increasing public concern. Therefore, constructing a simple, fast, effective, and low-cost rapid detection method has become an important issue in the field of food safety. Among them, aptasensors are emerging biosensors in the fields of food safety, detection and control. Nucleic acid aptamers (Nucleic acid aptamers) are single-stranded DNA or RNA sequences that specifically bind to proteins or other small molecules through systematic evolution of exponentially enriched ligands (SELEX) and other derivative technologies. Nucleic acid aptamers are widely used in food safety testing due to their wide range of target molecules, high sensitivity, strong specificity, and good stability. This article will review the latest research on aptamers of foodborne pathogenic bacteria, potential applications and optimization methods of aptasensors in foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Finally, we hope that this review can provide new ideas and approaches for the development and application of aptamer sensors for foodborne pathogenic bacteria.

Fig. 1. of paper.
2.Adapter
Fig. 2. , and of the . (A) of the . (B) . (C) the of the L3 by a , with from Ref (Ma et al., 2022). (D) of the by a 2′- O-RNA base, from Ref (Maio et al., 2017).
4. Combination of aptamers and biosensors

4.1 Application of aptamers in colorimetric sensors
Fig. 3. The -based . (A) based on label-free AuNPs (a), (b). (B) of for S., with from Ref (Wei et al., 2022). (C) n of the for of S. , from Ref (Yu et al., 2020).
4.2. Application of aptamers in fluorescence sensors
Fig. 4. The -based . (A) of the S. , with from Ref (Ren et al., 2019). (B) for V. , from Ref (Wu, 2019). (C) for E. , with from Ref (Yao et al., 2021).
4.3. Application of aptamers in electrochemical sensors
Fig. 5. The -based . (A) for of C. , with from Ref (Peng et al., 2019). (B) for B. , from Ref ( et al., 2019). (C) the of E. coli, with from Ref (Hua et al., 2018).
4.6 Zoom in

Fig. 6. The of the -based , and -based .(A) of V. , from Ref (Wu et al., 2015). (B) of P. , with from Ref (Xie etal., 2022). (C) for the of E. coli, from Ref (Yang et al., 2020).
5. Conclusion Future Prospects and Challenges
Foodborne pathogenic bacteria are an important threat to food safety. In summary, this article reviews the research progress of aptamers in food-borne pathogenic bacteria in recent years, as well as the application of aptamer sensors in the detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria. These aptamer-based biosensors exhibit good detection sensitivity, selectivity, and accuracy by introducing new signal transduction systems and multiple amplification strategies. We can find that colorimetric and fluorescent sensors have similar detection limits. But fluorescent sensors tend to have a larger detection range, while electrochemical sensors have the highest sensitivity and the lowest detection limit. However, during the application process, there are still some challenges that need to be solved in the application of these biosensors.
With the development of SELEX technology, the selection of faster and more accurate nucleic acid aptamers and a series of nucleic acid aptamer optimization methods are also conducive to obtaining more stable, better performance, higher affinity, and lower costs. of nucleic acid aptamers. Currently, in terms of aptamers, obtaining more stable and higher affinity aptamers is the direction of development. To achieve this goal, analyzing the specific binding sites of bacterial aptamers and the specific components of bacterial whole cells has become a key issue. However, due to the complexity of bacteria, there are few studies on the analysis of aptamer-bacterial binding sites and the molecular resolution of bacterial-aptamer binding. In order to solve the above problems, the application of computational prediction tools has become particularly important. In addition to using computers for primary sequence analysis, two-dimensional and three-dimensional structure prediction, how to complete the docking of complex targets such as food-borne pathogenic bacteria and aptamers and conduct corresponding molecular dynamics simulations to more accurately evaluate aptamers The stability of the body-target complex and determining its binding energy are also future considerations. Continuing developments along this direction could enhance the practical significance of aptamers.
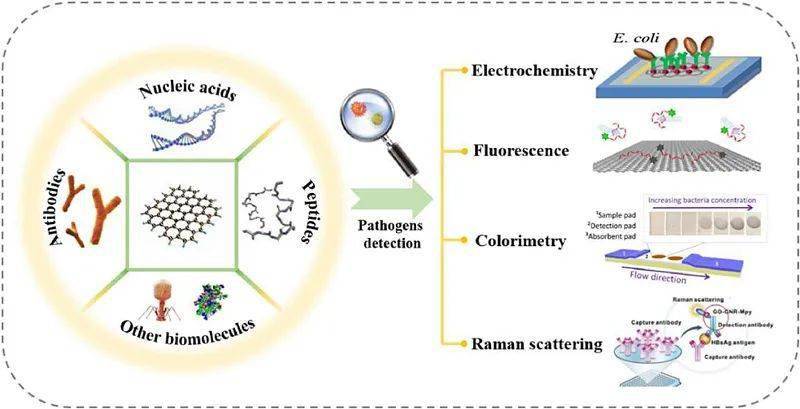
In terms of sensors, aptamer sensors targeting the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria have been a hot research topic in recent years. Optical aptamer sensors can detect changes in color or absorbance by direct observation. The electrochemical aptasensor has high sensitivity. A large number of papers have been published in this field, but most of them are verification of conceptual models and lack the potential for clinical practice. Therefore, it is necessary to improve aptasensor technology and sensor practicality. On the one hand, due to the complex composition of actual samples and the influence of environmental factors, the structure and properties of aptamers will change. Such as protein, lipid carbohydrates, pH and temperature, etc.
Nonspecific binding of aptamers may also lead to false-positive results, a phenomenon known as matrix effect. For example, target substances in milk can easily combine with other proteins to form polymers, thus affecting the detection results. This problem is often solved by diluting the sample before analysis or by protein precipitation. However, both processes are time-consuming. Therefore, it is necessary to study the effects of environmental factors, actual sample compositions of proteins and lipids on aptamer-target binding to guide the application of aptamers in detection systems. On the other hand, detected foodborne pathogens can present false positives due to mutations. Selecting aptamers that target specific components of bacteria can help avoid mutations. For example, bacteria can be identified through targeted screening of aptamers targeting specific proteins or polysaccharide components.
Sensors with high sensitivity are usually achieved by using one or more signal amplification methods. However, different amplification methods also have their limitations. Magnetic enrichment of magnetic species may affect signal intensity, and combination with enzymatic reactions may hinder the sensor's ability to function optimally in real-world and complex samples. The main challenge with nanomaterials is ensuring sensor stability and fabrication reproducibility. The solution to these problems is also the future development direction of fitness sensors.
Original link:
Online submission platform link: